Sesamoid Bone injury
🦶 Foot Sesamoid Bone Injuries: Types & Key Insights
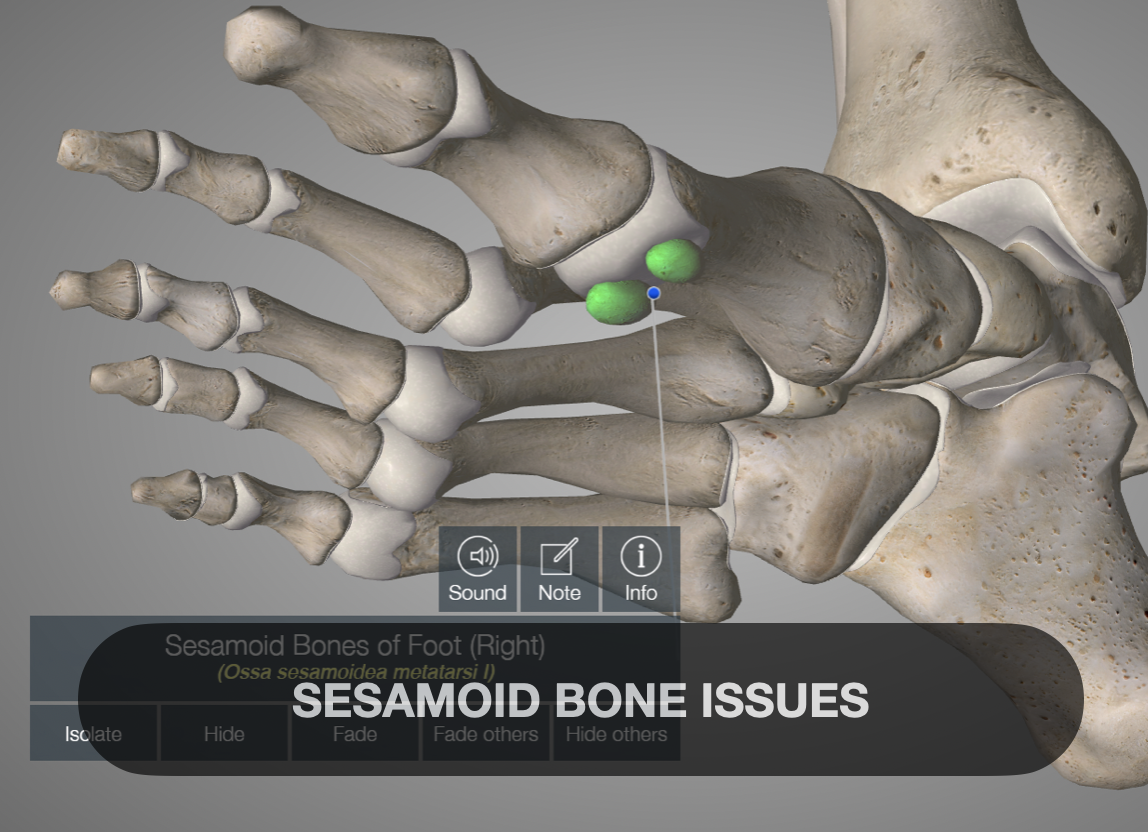
🦴 Anatomy & Function
The foot typically contains two sesamoid bones beneath the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, embedded within tendons of the flexor hallucis brevis muscle.
These bones act as pulleys, facilitating toe movement and absorbing weight during activities like walking and running.
🔄 Injury Types
Sesamoiditis (Inflammation)
An overuse injury causing inflammation of the sesamoid bones and surrounding tendons.
Common in athletes engaging in high-impact activities that stress the ball of the foot.
Symptoms include pain in the forefoot, swelling, and tenderness, especially during weight-bearing activities.
Treatment typically involves rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and modifications in footwear.
Sesamoid Fractures
Can be acute (due to trauma) or stress-related (from repetitive stress).
Stress fractures are more common in the tibial sesamoid.
Symptoms include pain during movement of the big toe, swelling, and tenderness in the midfoot.
Diagnosis is confirmed through imaging, and treatment may involve rest, immobilization, or surgical intervention in severe cases.
Bipartite Sesamoid
A congenital condition where the sesamoid bone is divided into two parts.
Often asymptomatic but can cause pain if the parts are displaced or irritated.
Treatment may include conservative measures or surgery if symptomatic.
Turf Toe
Injury to the soft tissues surrounding the big toe joint, often from hyperextension.
Common in athletes who push off forcefully during play.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited range of motion in the big toe.
Treatment involves rest, ice, and possibly immobilization.
Osteonecrosis
A rare condition where blood flow to the sesamoid bone is disrupted, leading to bone death.
Symptoms include persistent pain and swelling.
Diagnosis is through imaging, and treatment may involve rest, medication, or surgical intervention.
I